Welcoming a newborn is an incredible experience, but seeing your baby’s skin or eyes turn yellow can be scary. If you’re wondering what newborn jaundice is and how to care for it, you’re not alone.
Understanding the signs and knowing what steps to take can make all the difference for your baby’s health. You’ll discover simple, clear advice to help you manage newborn jaundice with confidence and ease. Keep reading to learn how to protect your little one and bring peace of mind to your family.

Causes Of Newborn Jaundice
Newborn jaundice occurs when a baby’s skin and eyes turn yellow. This yellow color happens because of a substance called bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin forms when the body breaks down old red blood cells. Babies have more red blood cells than adults, so their bodies make more bilirubin. Their livers may not be ready to remove bilirubin fast enough. This causes bilirubin to build up, leading to jaundice.
What Triggers Jaundice In Newborns
Jaundice can start for different reasons. Many newborns have a natural build-up of bilirubin. This is called physiological jaundice. It usually appears two to four days after birth. Some babies get jaundice because their liver is immature. Other causes include bruising during birth or not feeding well. Poor feeding can reduce the baby’s ability to pass bilirubin through stool.
Types Of Jaundice
There are several types of jaundice in newborns. Physiological jaundice is the most common and mild. Breastfeeding jaundice happens when babies don’t get enough milk. Breast milk jaundice appears after the first week and lasts longer. Pathological jaundice is more serious and happens soon after birth. It may need medical care. Each type has different causes and treatments.
Risk Factors To Watch
Some babies have a higher chance of jaundice. Premature babies often face jaundice because their livers are less developed. Babies with a family history of jaundice are at risk. Blood type differences between mother and baby can cause jaundice too. Other risks include infections and bruising during delivery. Watching these factors helps doctors care for babies early.

Symptoms To Spot Early
Newborn jaundice is common but needs careful watching. Spotting symptoms early helps protect your baby’s health. Knowing what to watch for can make a big difference.
Signs Of Jaundice In Babies
Yellow skin is the most common sign of jaundice. It usually starts on the face and spreads to the chest and legs. Look at the whites of your baby’s eyes. They may turn yellow too. The baby might be very sleepy or hard to wake. Sometimes, feeding becomes difficult or less frequent. Pale or dark urine and light-colored stools may also appear. These signs show that bilirubin levels are high and need attention.
When To Seek Medical Help
Contact a doctor if yellow color spreads quickly or gets darker. Call if your baby is very sleepy and does not feed well. Seek help if your baby has trouble breathing or is very fussy. Persistent vomiting or fever needs immediate medical care. Early treatment prevents serious problems. Always trust your instincts and act fast.
Home Care Tips
Newborn jaundice needs careful attention at home. Parents play a big role in helping their baby recover. Small actions can support the baby’s health and comfort. Here are some simple tips for home care.
Feeding Practices To Support Recovery
Feed your baby often. Breastfeeding helps flush out bilirubin through urine and stool. Aim for at least 8 to 12 feedings in 24 hours. Keep the baby well-hydrated to prevent dehydration. Watch for signs of hunger and feed promptly. If breastfeeding is hard, talk to a healthcare provider.
Safe Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight can help lower bilirubin levels. Place your baby near a sunny window for 10 to 15 minutes daily. Avoid direct sun to protect delicate skin. Morning or late afternoon light is best. Use a thin cloth to cover the baby’s eyes. Never use sunlight as the only treatment.
Monitoring Baby’s Behavior
Check your baby’s skin and eyes for yellow color daily. Notice if your baby is sleepy or hard to wake. Watch for poor feeding or unusual fussiness. Keep track of wet and dirty diapers. Report any worrying changes to your doctor quickly. Early detection helps prevent complications.
Medical Treatments Available
Newborn jaundice often needs treatment to keep the baby safe. Medical care helps lower high bilirubin levels quickly. Treatment depends on how severe the jaundice is. Doctors choose the best option to stop complications. Understanding these treatments helps parents feel more confident and prepared.
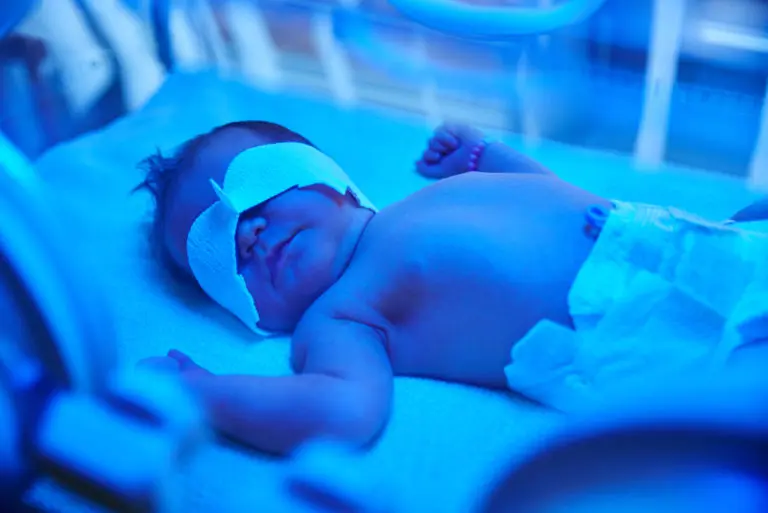
Phototherapy Explained
Phototherapy uses special blue lights to treat jaundice. The light changes bilirubin into a form the baby can easily pass. Babies lie under the light with their eyes protected. This treatment is painless and works fast. Doctors watch bilirubin levels to decide how long phototherapy lasts.
Other Treatment Options
In some cases, doctors use other treatments. A blood transfusion may be needed for very high bilirubin. This replaces the baby’s blood with fresh blood. Medicines can also help reduce bilirubin. Each treatment is chosen based on the baby’s health and jaundice level.
Follow-up Care Guidelines
After treatment, babies need regular check-ups. Doctors check bilirubin levels to ensure they stay low. Parents should watch for yellow skin or eyes. Feeding the baby well helps remove bilirubin faster. Follow-up care keeps the baby safe and healthy.
Preventing Jaundice Recurrence
Preventing jaundice recurrence in newborns is very important for their health. Jaundice can come back if not managed well after the first episode. Parents and caregivers must follow key steps to keep the baby safe and healthy. These steps include feeding habits, regular checkups, and hydration.
Breastfeeding Strategies
Feed your baby often to help flush out bilirubin. Frequent breastfeeding helps the baby pass stools, which removes excess bilirubin. Aim for feeding at least 8 to 12 times in 24 hours. Watch for good latch and proper milk flow. If breastfeeding is difficult, consult a lactation expert quickly.
Regular Health Checkups
Schedule regular visits with the pediatrician. Doctors check the baby’s skin color and bilirubin levels. Early detection helps prevent jaundice from returning. Follow the doctor’s advice on blood tests and treatment plans. Keep all appointments to track the baby’s progress closely.
Maintaining Hydration
Keep your newborn well hydrated to support liver function. Fluids help the body process and remove bilirubin. Breast milk is the best source of hydration. Avoid giving water unless the doctor says so. Proper hydration keeps the baby healthy and lowers jaundice risks.
Parental Support And Resources
Newborn jaundice can be stressful for parents. Support and good resources help parents care for their baby better. Learning about jaundice and knowing where to find help makes a big difference. This section highlights places and tools parents can use for support.
Community And Online Support
Many parents find comfort in sharing experiences with others. Online groups and forums offer a place to talk and ask questions. Local parent groups sometimes hold meetings or offer advice. These communities help parents feel less alone and more confident.
Helpful Tools And Apps
Apps can track your baby’s health and jaundice symptoms. Some apps remind parents about feeding times and doctor visits. They also provide easy tips for jaundice care. Using these tools keeps parents organized and informed every day.
When To Consult A Specialist
Some jaundice cases need expert care. Signs like very yellow skin or poor feeding need quick attention. Specialists can test bilirubin levels and suggest treatments. Parents should watch for changes and contact a doctor if worried.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Common Symptoms Of Newborn Jaundice?
Newborn jaundice shows as yellowing of the skin and eyes. It often appears within the first week. Babies may seem sleepy or feed poorly. Early detection helps in effective treatment and preventing complications.
How Is Newborn Jaundice Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose jaundice by checking skin and eye color. A blood test measures bilirubin levels to confirm jaundice. Sometimes a skin test with a special device is used. Prompt diagnosis ensures timely care and management.
What Treatments Are Available For Newborn Jaundice?
Mild jaundice often resolves with regular feeding and sunlight exposure. Moderate to severe cases require phototherapy, using special light to reduce bilirubin. In rare cases, blood transfusion is needed. Treatment choice depends on bilirubin levels and baby’s health.
How Can Parents Prevent Newborn Jaundice Worsening?
Ensure frequent breastfeeding to help bilirubin elimination. Monitor baby’s skin color and behavior closely. Seek medical advice if yellowing spreads or baby is lethargic. Early care prevents complications and supports healthy recovery.
Conclusion
Caring for newborn jaundice needs gentle and steady attention. Watch your baby’s skin and eyes for yellow signs. Feed your baby well to help clear jaundice faster. Keep all doctor visits on time. Early care can prevent serious problems. Trust your instincts and ask for help if unsure.
Small steps make a big difference in healing. Your love and care support your baby’s health every day. Stay calm and patient through this phase. Bright days will come with good care and rest.

